JDBC in Wallboard
Using this feature requires advanced knowledge. It is designed primarily for custom projects and does not come with standard support.
We recommend contacting our support team and requesting professional services before proceeding with integration.
Java Database Connectivity, or JDBC for short, is an API for the Java programming language that allows database access. JDBC defines the classes and methods required to query and modify databases. Adapts to the relational data model.
If you want to use JDBC in our system, you need to know some basic JPQL syntax.
Like [SELECT…], [WHERE…], [GROUP BY…], [ORDER BY…]..etc.
Set up connector
You can set up the connector in Administrator > JDBC drivers where you can add new drivers with the + button.
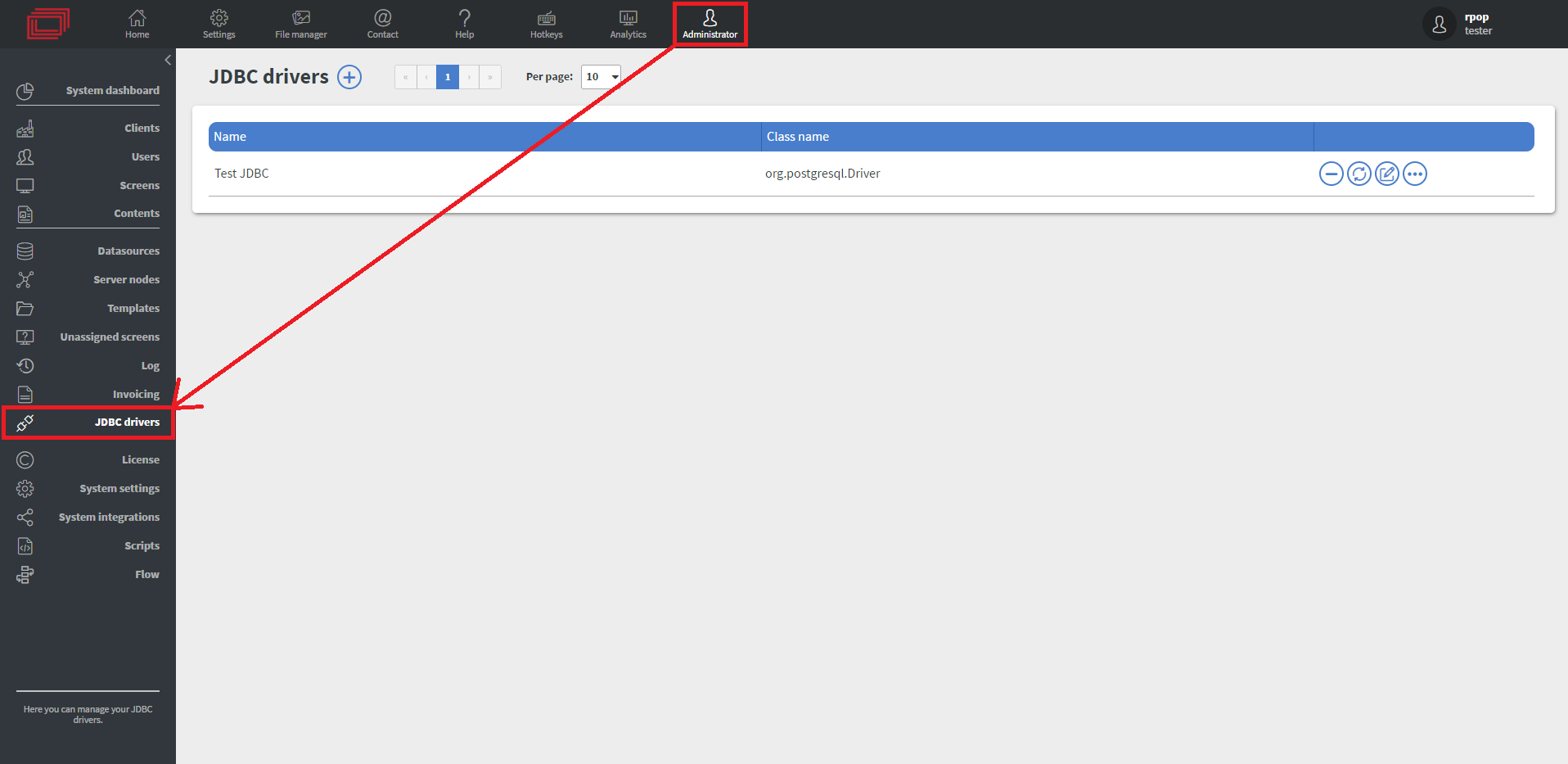
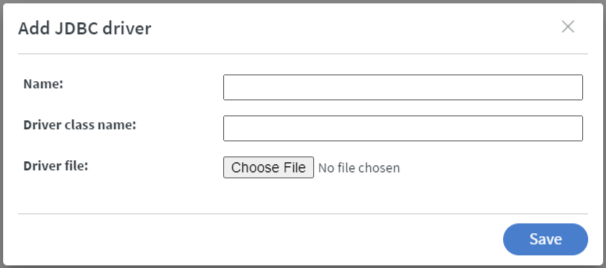
- There you can give your JDBC driver a
NamelikeTest JDBC. - You need to give the
Driver class namein our example it will beorg.postgresgl.Driver- You can find the driver class name in most cases from the driver provider.
- Lastly, you need to pick your .jar file our example is a connector for postgresql
After all these steps, your JDBC driver is ready to use.
You can upload as many drivers as you want, and java will automatically decide which one to use for any given database.
Set up datasource
You can create a datasource with the new driver and it will give you back your query result as JSON.
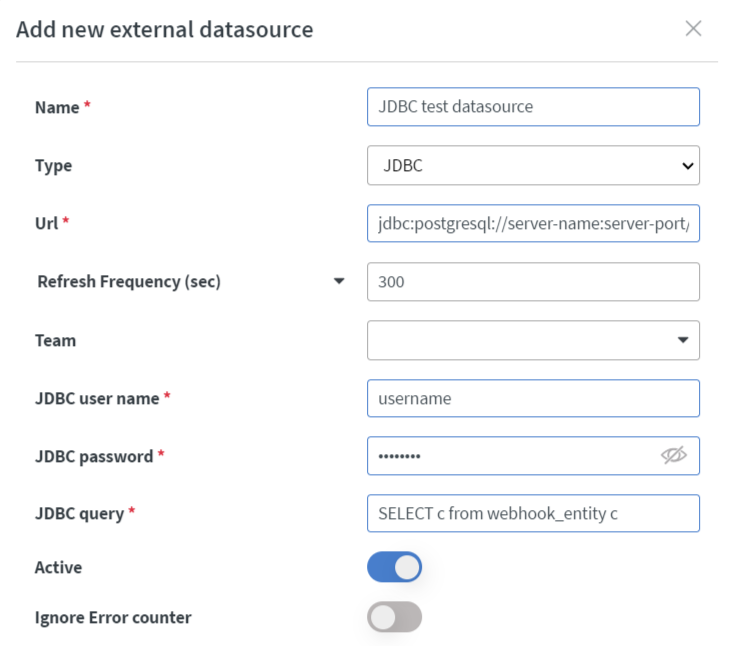
- You need to fill the URL with URL Connection String.
- Our example uses postgresql so the string should look like: jdbc:postgresql://server-name:server-port/database-name
- The sting does not necessarily need to include the name of the driver. Drivers are usually accompanied by an example of what the associated url string is.
- You need to set the
TypetoJDBC. - Fill
JDBC user name,JDBC passwordfields with the correct credentials. - In the end, you need to define a query in the JDBC query field.
Here are some examples for our prostgresql query:
SELECT t
FROM table t
SELECT t
FROM table t
WHERE t.id = 2
SELECT t
FROM table t
WHERE t.id = 2
GROUP BY id
SELECT t
FROM table t
WHERE t.id = 2
GROUP BY id
ORDER BY id DESC
After all these steps, your JDBC datasource is ready to use.